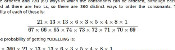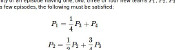Blog
Countdown probability, pt. 2
2014-04-11
As well as letters games, the contestants on Countdown also take part in numbers games. Six numbers are chosen from the large numbers (25,50,75,100) and small numbers (1-10, two cards for each number) and a total between 101 and 999 (inclusive) is chosen by CECIL. The contestants then use the six numbers, with multiplication, addition, subtraction and division, to get as close to the target number as possible.
The best way to win the numbers game is to get the target exactly. This got me wondering: is there a combination of numbers which allows you to get every total between 101 and 999? And which combination of large and small numbers should be picked to give the highest chance of being able to get the target?
To work this out, I got my computer to go through every possible combination of numbers, trying every combination of operations. (I had to leave this running overnight as there are a lot of combinations!)
Getting every total
There are 61 combinations of numbers which allow every total to be obtained. These include the following (click to see how each total can be made):
- 5 6 8 9 10 100
- 5 6 7 8 10 100
- 4 6 7 8 9 100
- 3 6 7 8 10 100
- 3 5 7 8 9 100
- 2 5 6 8 9 100
- 2 6 7 8 9 100
- 5 6 8 9 75 100
- 3 6 8 10 75 100
- 2 6 9 10 75 100
By contrast, the following combination allows no totals between 101 and 999 to be reached:
- 1 1 2 2 3 3
The number of attainable targets for each set of numbers can be found here.
Probability of being able to reach the target
Some combinations of numbers are more likely than others. For example, 1 2 25 50 75 100 is four times as likely as 1 1 25 50 75 100, as (ignoring re-orderings) in the first combination, there are two choices for the 1 tile and 2 tile, but in the second combination there is only one choice for each 1 tile. Different ordering of tiles can be ignored as each combination with the same number of large tiles will have the same number of orderings.
By taking into account the relative probability of each combination, the following probabilities can be found:
| Number of large numbers | Probability of being able to reach target |
| 0 | 0.964463439 |
| 1 | 0.983830962 |
| 2 | 0.993277819 |
| 3 | 0.985770510 |
| 4 | 0.859709475 |
So, in order to maximise the probability of being able to reach the target, two large numbers should be chosen.
However, as this will mean that your opponent will also be able to reach the target, a better strategy might be to pick no large numbers or four large numbers and get closer to the target than your opponent, especially if you have practised pulling off answers like this.
Edit: Numbers corrected.
Edit: The code used to calculate the numbers in this post can now be found here.
(Click on one of these icons to react to this blog post)
You might also enjoy...
Comments
Comments in green were written by me. Comments in blue were not written by me.
2016-07-20
@Francis Galiegue: I've pushed a version of the code to https://github.com/mscroggs/countdown-...Matthew
@Francis Galiegue: Sadly, I lost the code I used when I had laptop problems. However, I can remember what it did, so I shall recreate it and put it on GitHub.
Matthew
If you could, I'd love to have the code you used to do this exhaustive search?
I'm a fan of the game myself (but then I'm French, so to me it's the original, "Des chiffres et des lettres"), but for the numbers game, this is pretty much irrelevant to the language and country :)
I'm a fan of the game myself (but then I'm French, so to me it's the original, "Des chiffres et des lettres"), but for the numbers game, this is pretty much irrelevant to the language and country :)
Francis Galiegue
Add a Comment