Blog
2016-03-31
Pythagoras's Theorem is perhaps the most famous theorem in maths. It is also very old, and for over 2500 years mathematicians have been explaining why it is true.
This has led to hundreds of different proofs of the theorem. Many of them were collected in the 1920s in The pythagorean proposition by Elisha Scott Loomis [1]. Let's have a look at some of them.
Using similar triangles
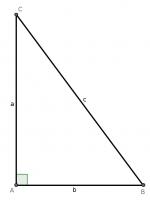
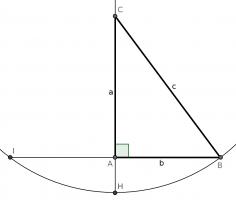
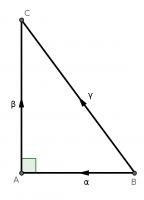
For our first proof, start with a right angled triangle, \(ABC\), with sides of lengths \(a\), \(b\) and \(c\).
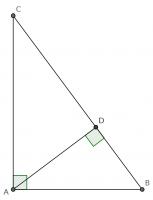
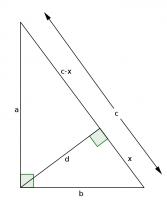
Add a point \(D\) on the hypotenuse such that the line \(AD\) is perpendicular to \(BC\). Name the lengths as shown in the second diagram.
\(ABC\) and \(DBA\) are similar triangles, so:
$$\frac{b}{x}=\frac{c}{b}$$
$$b^2=xc$$
\(ABC\) and \(DAC\) are similar triangles, so:
$$\frac{a}{c-x}=\frac{c}{a}$$
$$a^2=c^2-cx$$
Adding the two equations gives:
$$a^2+b^2=c^2$$
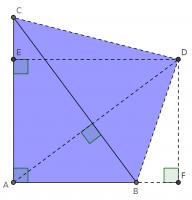
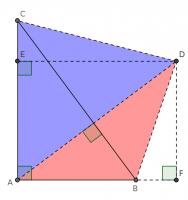
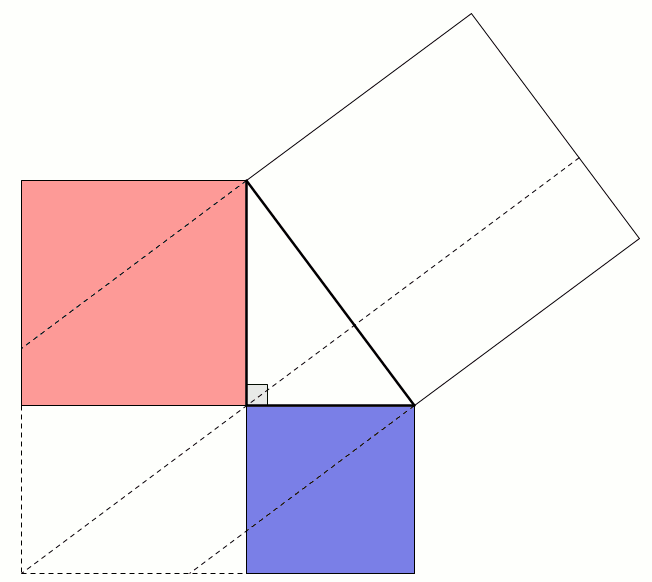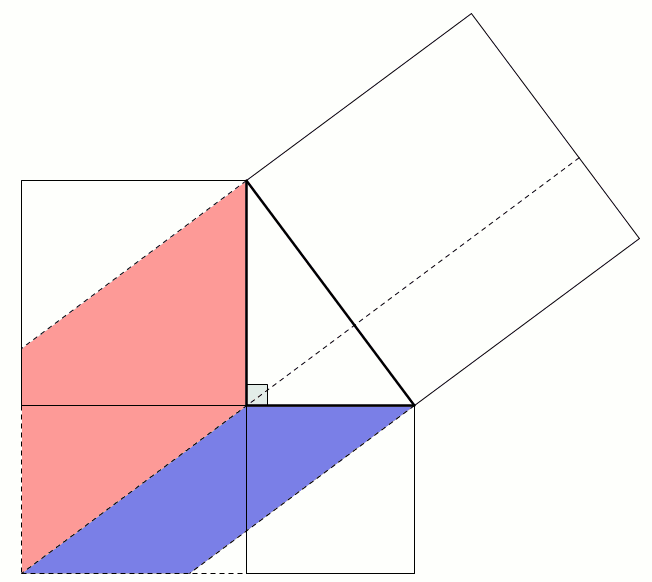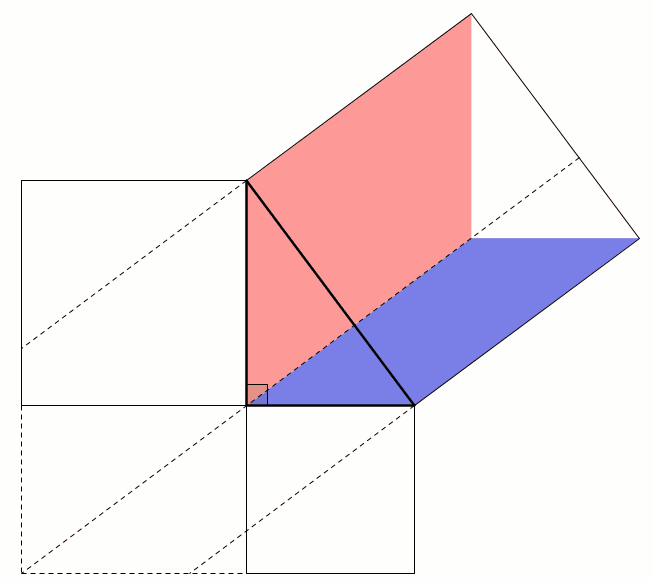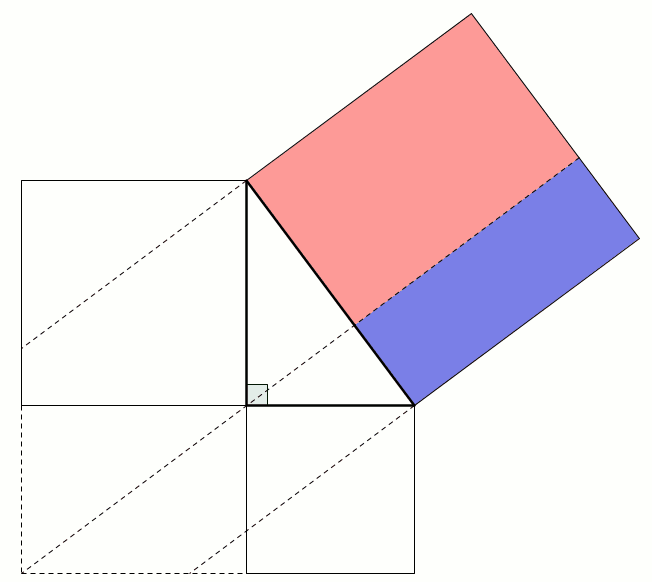
Constructing a quadrilateral
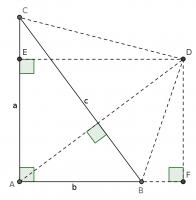
This proof shows the theorem is true by using extra lines and points added to the triangle. Start with \(ABC\) as before then add a point \(D\) such that \(AD\) and \(BC\) are perpendicular and of equal length. Add points \(E\) on \(AC\) and \(F\) on \(AB\) (extended) such that \(DE\) and \(AC\) are perpendicular and \(DF\) and \(AB\) are perpendicular.
By similar triangles, it can be seen that \(DF=b\) and \(DE=a\).
As the two diagonals of \(BACD\) are perpendicular, its area is \(\tfrac12c^2\).
The area of \(BACD\) is also equal to the sum of the areas of \(ABD\) and \(ACD\). The area of \(ABD\) is \(\tfrac12b^2\). The area of \(ACD\) is \(\tfrac12a^2\).
Therefore, \(\tfrac12a^2+\tfrac12b^2=\tfrac12c^2\), which implies that \(a^2+b^2=c^2\).
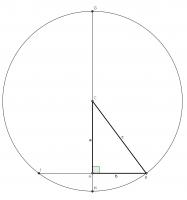
Using a circle
This proof again uses extra stuff: this time using a circle. Draw a circle of radius \(c\) centred at \(C\). Extend \(AC\) to \(G\) and \(H\) and extend \(AB\) to \(I\).
By the intersecting chord theorem, \(AH\times AG = AB\times AI\). Using the facts that \(AI=AB\) and \(CH\) and \(CG\) are radii, the following can be obtained from this:
$$(c-a)\times(c+a)=b\times b$$
$$c^2-a^2=b^2$$
$$a^2+b^2=c^2$$
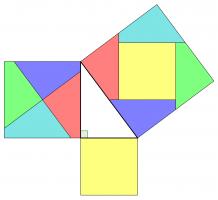
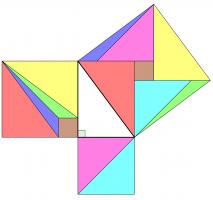
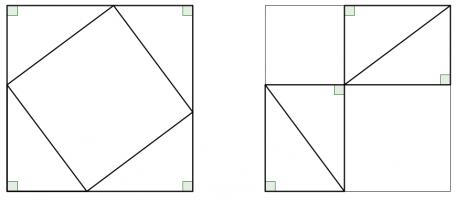
Rearrangement proofs
A popular method of proof is dissecting the smaller squares and rearranging the pieces to make the larger square. In both the following, the pieces are coloured to show which are the same:
Alternatively, the theorem could be proved by making copies of the triangle and moving them around. This proof was presented in The pythagorean proposition simply with the caption "LOOK":
This next proof uses the fact that two parallelograms with the same base and height have the same area: sliding the top side horizontally does not change the area. This allows us to move the smaller squares to fill the large square:
For this proof, start by labelling the sides of the triangle as vectors \(\alpha\), \(\beta\) and \(\gamma\).
Clearly, \(\gamma = \alpha+\beta\). Taking the dot product of each side with itself gives:
$$\gamma\cdot\gamma = \alpha\cdot\alpha+2\alpha\cdot\beta+\beta\cdot\beta$$
\(\alpha\) and \(\beta\) are perpendicular, so \(\alpha\cdot\beta=0\); and dotting a vector with itself gives the size of the vector squared, so:
$$|\gamma|^2=|\alpha|^2+|\beta|^2$$
If you don't like any of these proofs, there are of course many, many more. Why don't you tweet me your favourite.
References
(Click on one of these icons to react to this blog post)
You might also enjoy...
Comments
Comments in green were written by me. Comments in blue were not written by me.
Add a Comment