Blog
Off-by-one errors
2022-12-29
This is the 100th blog post on this website!
But if I hadn't pointed this out,
you might not have noticed: the URL of the page is mscroggs.co.uk/blog/99 and not mscroggs.co.uk/blog/100.
This is a great example of an off-by-one error.
Off-by-one errors are one of the most common errors made when programming and elsewhere, and this is an excellent opportunity to blog about them.
Fence posts and fence panels
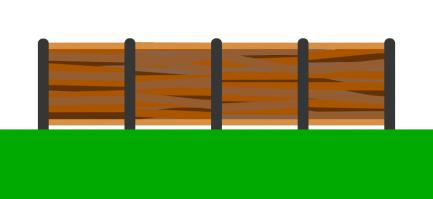
Imagine you want to make a straight fence that is 50m long. Each fencing panel is 2m long.
How many fence posts will you need?
Have a quick think about this before reading on.
If you're currently thinking about the number 25, then you've just made an off-by-one error.
The easiest way to see why is to think about some shorter fences.
If you want to make a fence that's 2m long, then you'll need just one fence panel. But one fence
post will not be enough: you'll need a second post to put at the other end of the fence panel.
If you want to make a 4m long fence, you'll need a post before the first panel, a post between
the two panels, and a post after the second panel: that's three posts in total.
In general, you'll always need one more fence post than panel, as you need a fence post
at the start of each panel and an extra post at the end of the final panel.
(Unless, of course, you're building a fence that is a closed loop.)
This fence post/fence panel issue appears surprisingly often, and can make counting things
quite difficult. For example, the first blog post
on this website was posted in 2012: ten years ago. But if you count the number of years listed in the
archive there are 11 years. If you release an issue of a magazine once a year, then issue 11 (not issue 10) will
be the issue released 10 years after you start not issue 10. If, like Chalkdust,
you release issues two times a year, issue 21 (not issue 20) will be the 10 year issue.
Half-open intervals
An interval is called closed if it includes its starting and ending point, and open if it
doesn't include them. A half-open interval includes one end point and not the other.
Using half-open intervals makes counting things less difficult: including one endpoint but not the other is a bit like ignoring
the final (or first) fence post so that there are the same number of post and panels.
In Python, the range function includes the first number but not the last
(this is the sensible choice as including the final number and not the first would be very confusing).
range(5, 8) includes the numbers 5, 6, and 7 (but not 8).
By excluding the final number, the number of numbers in a range
will be equal to the difference between the two input numbers.
Excluding the final item so that the number of items in a range is equal to the difference between the start and end is a great way to
reduce opportunities for off-by-one errors, and isn't too hard to get used to.
Why start at 0?
We've seen a couple of causes of off-by-one errors, but we've not yet seen why this page's URL
contains 99 rather than 100. This is because the numbering of blog posts started at zero.
But why is it a sensible choice to start at 0?
Using a half-open range, the first \(n\) numbers starting at 1 would be range(1, n + 1); the first \(n\) numbers starting at 0 on the other hand
would be range(0, n). The second option is neater, as you don't have to add one to the final number; the first option opens up more opportunities for
off-by-one errors.
This is one of the reasons why Python and many other programming languages start their numbering from 0.
Why doesn't everyone start at 0?
Starting at 0 and using half-open intervals to represent ranges of integers seem like good ways to help people avoid making off-by-one errors, but this choice is not perfect.
If you want to write a range of numbers from 1 to 8 inclusive using this convention, you would have to write range(1, 9):
forgetting to add one to the final number in this situation is another source of off-by-one errors.
It's also more natural to many people to start counting from 1, so some programming languages choose different conventions. The following table sums up the different possible
conventions, which desirable properties they have, and which languages use them.
| Convenction | Languages using this convention | Length of range is difference between endpoints | range(START, n) contains \(n\) numbers | range(START, n) contains START | range(START, n) contains \(n\) |
| START=0, range includes first endpoint only | Python, Javascript, PHP, Rust, C, C++ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ |
| START=0, range includes last endpoint only | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | |
| START=0, range includes both endpoints | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| START=0, range includes neither endpoint | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | |
| START=1, range includes first endpoint only | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | |
| START=1, range includes last endpoint only | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | |
| START=1, range includes both endpoints | Matlab, Julia, Fortran | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| START=1, range includes neither endpoint | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ |
(I don't know of any languages that use any of the other conventions, but if you have please let me know in the comments below and I'll add them.)
None of the conventions manages to remove all the possible sources of confusion, so it looks like off-by-one errors are here to stay.
(Click on one of these icons to react to this blog post)
You might also enjoy...
Comments
Comments in green were written by me. Comments in blue were not written by me.
Add a Comment




Love your blog posts!
They make me get out of bed in the morning.
Just wanted to show my appreciation.
Cheers.