Blog
2019-12-27
In tonight's Royal Institution Christmas lecture,
Hannah Fry and Matt Parker demonstrated how machine learning works using MENACE.
The copy of MENACE that appeared in the lecture was build and trained by me. During the training, I logged all the moved made by MENACE and the humans playing against them, and using this data I have
created some visualisations of the machine's learning.
First up, here's a visualisation of the likelihood of MENACE choosing different moves as they play games. The thickness of each arrow represented the number of beads in the box corresponding to that move,
so thicker arrows represent more likely moves.
The likelihood that MENACE will play each move.
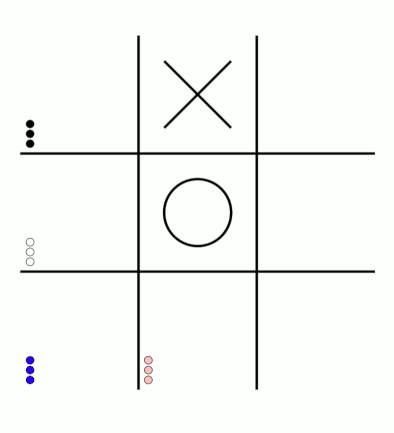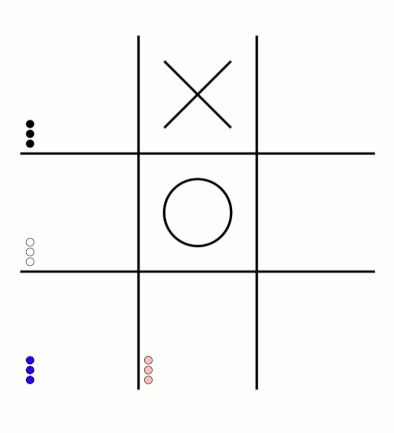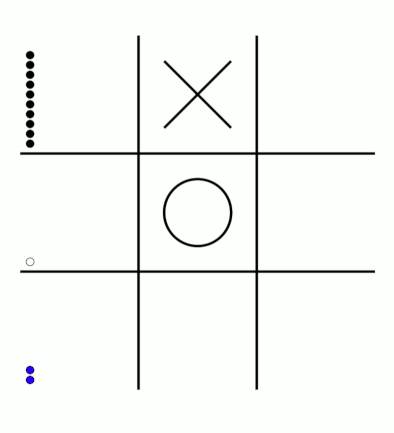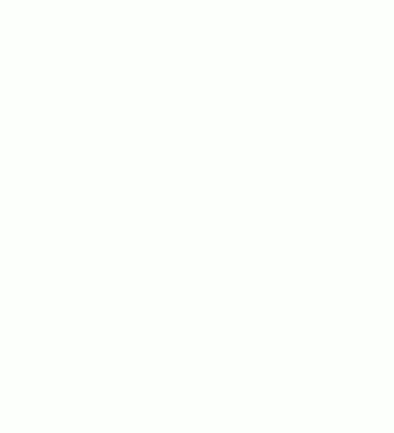
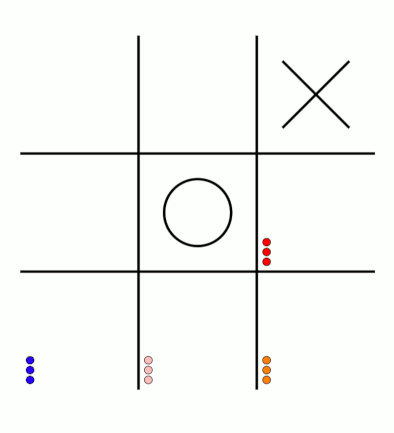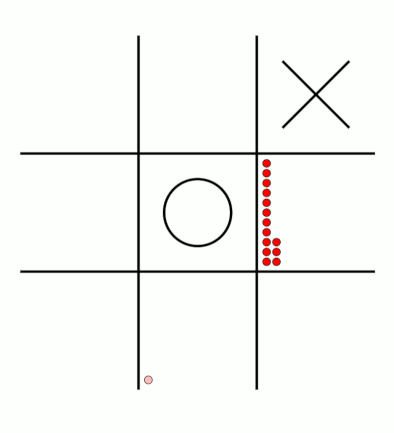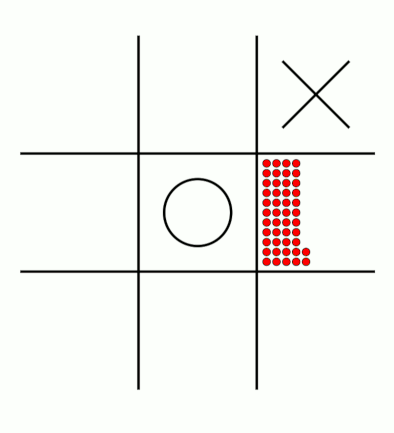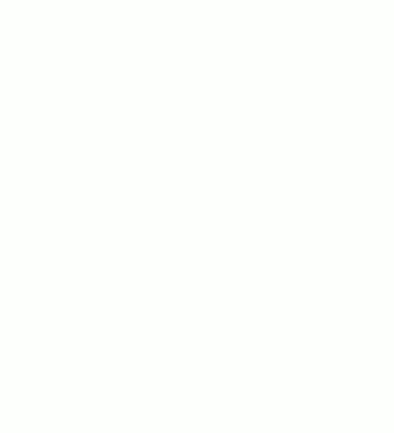
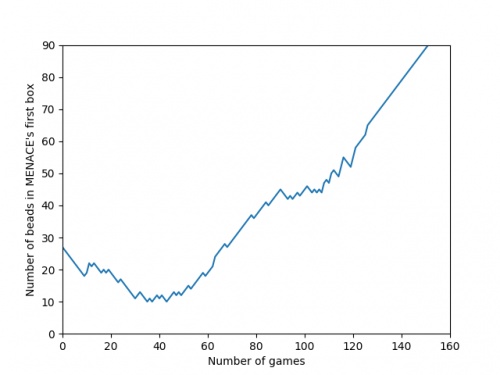
There's an awful lot of arrows in this diagram, so it's clearer if we just visualise a few boxes. This animation shows how the number of beads in the first box changes over time.
You can see that MENACE learnt that they should always play in the centre first, an ends up with a large number of green beads and almost none of the other colours. The following
animations show the number of beads changing in some other boxes.
MENACE learns that the top left is a good move.
MENACE learns that the middle right is a good move.
MENACE is very likely to draw from this position so learns that almost all the possible moves are good moves.
The numbers in these change less often, as they are not used in every game: they are only used when the game reached the positions shown on the boxes.
We can visualise MENACE's learning progress by plotting how the number of beads in the first box changes over time.
Alternatively, we could plot how the number of wins, loses and draws changes over time or view this as an animated bar chart.
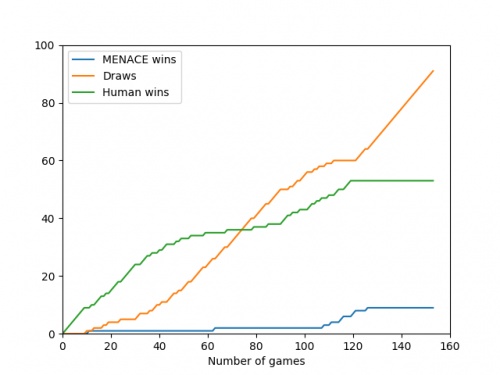
The number of games MENACE wins, loses and draws.
The number of games MENACE has won, lost and drawn.
If you have any ideas for other interesting ways to present this data, let me know in the comments below.
(Click on one of these icons to react to this blog post)
You might also enjoy...
Comments
Comments in green were written by me. Comments in blue were not written by me.
I have played around menace a bit and frankly it doesnt seem to be learning i occasionally play with it and it draws but againt the perfect ai you dont see as many draws, the perfect ai wins alot more
(anonymous)
@Colin: You can set MENACE playing against MENACE2 (MENACE that plays second) on the interactive MENACE. MENACE2's starting numbers of beads and incentives may need some tweaking to give it a chance though; I've been meaning to look into this in more detail at some point...
Matthew
Idle pondering (and something you may have covered elsewhere): what's the evolution as MENACE plays against itself? (Assuming MENACE can play both sides.)
Colin
Add a Comment

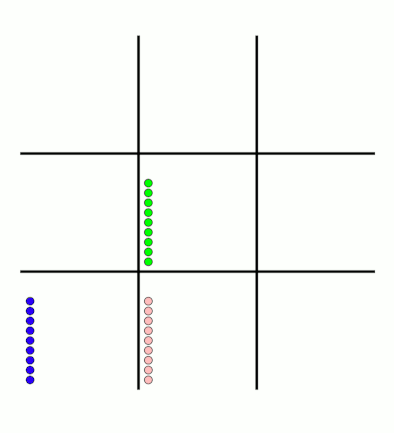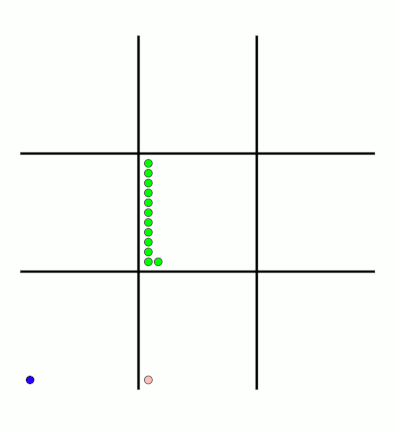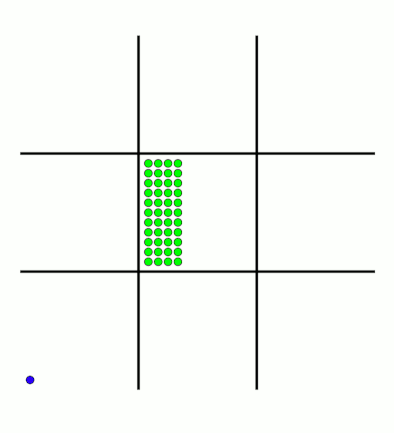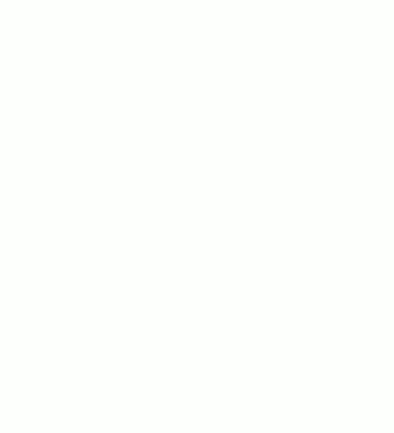
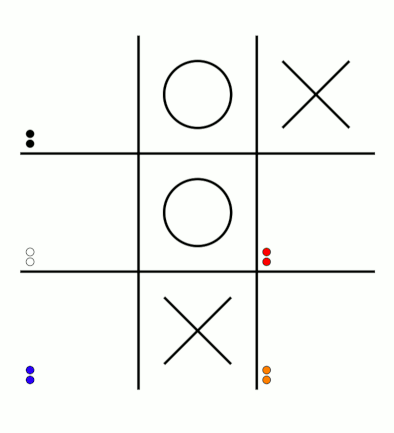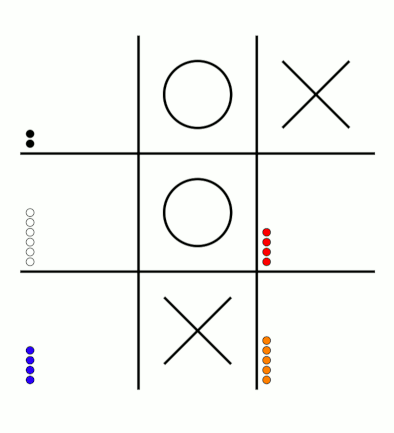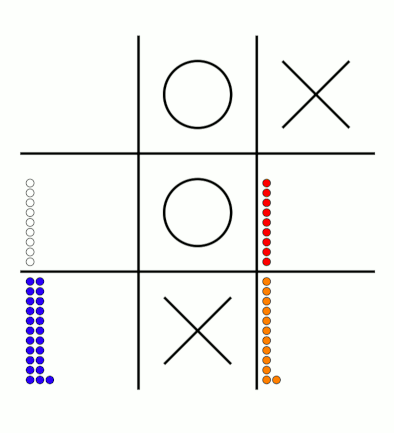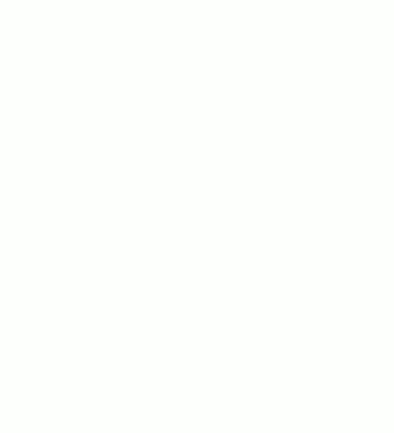
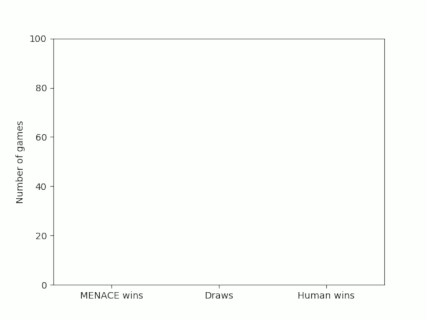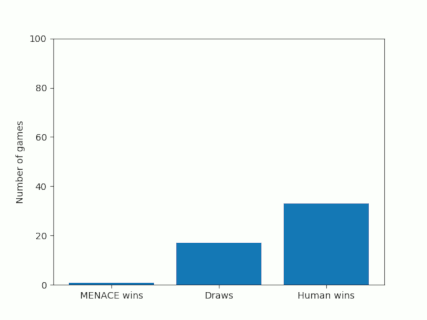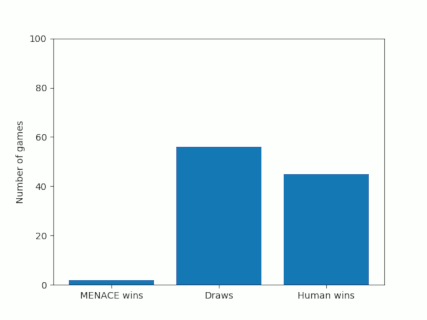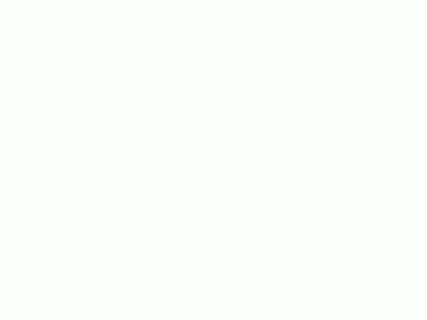




It takes around 80 games for MENACE to learn against the perfect AI. So it could be you've not left it playing for long enough? (Try turning the speed up to watch MENACE get better.)